Retinal Tears
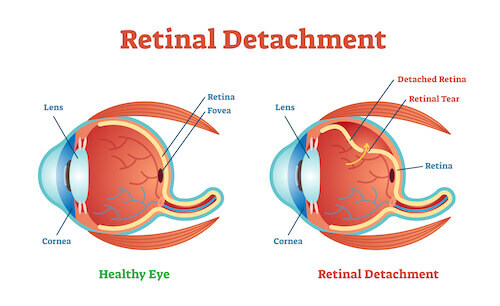
The retina is the inner lining of the eye; it is the thin, light-sensitive tissue that generates vision. Tears can form in the retina, creating a risk of retinal detachment and severe loss of vision.
Symptoms
A patient with an acute retinal tear may experience the sudden onset of black spots or “floaters” in the affected eye. This can have the appearance of someone shaking pepper in your vision. Flashes of light (Photopsia) are another common symptom.
If there is associated vitreous hemorrhage (bleeding in the clear cavity of the eye) or retinal detachment, additional symptoms can include blurred vision or a shadow as if curtains are closing in from the peripheral (side) vision. However, in some cases, a retinal tear may not manifest any noticeable symptoms.
Causes
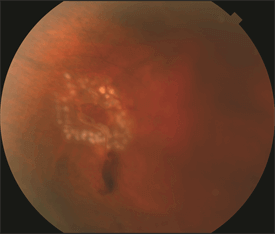
The vitreous is a clear gel-like substance that fills in the back cavity of the eye which is lined by the retina. At birth, this gel is attached to the retina, but as we age, the gel separates from the retina creating a posterior vitreous detachment or PVD. In most cases, this happens without any issue.
However, in people who have an inherently more “sticky” vitreous, as the vitreous separates from the retina, it pulls abnormally (abnormal vitreo-retinal adhesion) and causes the retina to tear. Although retinal tears may also occur as a result of eye trauma, most retinal tears occur spontaneously due to a PVD.retina. At birth, this gel is attached to the retina, but as we age, the gel separates from the retina creating a posterior vitreous detachment or PVD. In most cases, this happens without any issue.
Risk Factors
Risk factors are not required to develop a retinal tear, but they make the likelihood greater. These factors include:
- Advanced age
- Degree of myopia (nearsightedness)
- Associated lattice degeneration (thin patches in the retina)
- Trauma
- Family history of retinal tears or detachment
- Prior eye surgery
There is no way to predict who might develop a retinal tear or when it might occur.
Diagnostic Testing
A thorough and timely examination by an ophthalmologist using scleral depression (applying slight pressure to the eye) and/or a 3-mirror lens is the most important step in diagnosing a retinal tear. In cases where there is a limited view of the retina due to overlying hemorrhage, ophthalmic ultrasound may be required to aid in diagnosing a retinal tear.
Treatment and Prognosis
If a retinal tear is diagnosed promptly before it progresses to retinal detachment, the prognosis is extremely good. Retinal tears are typically treated with laser or a freezing procedure (cryotherapy). Treatment is performed in an office setting and is very effective and quite safe.
Topical or local anesthesia is utilized, and the procedure is only mildly uncomfortable. The treatment creates spot-welding around the edges of the tear that nearly eliminates the risk of the tear progressing to retinal detachment. After a tear has been treated, there remains a future risk of developing additional, separate retinal tears; therefore, continued monitoring is important.
Not all retinal tears require treatment. When low-risk tears are identified in patients who have no symptoms, these tears can be observed without treatment. Some tears “treat themselves,” meaning they develop adhesion around the tear without treatment, and these situations can be followed without treatment as well.
Retinal Detachment
The retina lines the back wall of the eye, and is responsible for absorbing the light that enters the eye and converting it into an electrical signal that is sent to the brain via the optic nerve, allowing you to see. Many conditions can lead to a retinal detachment, in which the retina separates from the back wall of the eye, like wallpaper peeling off a wall.
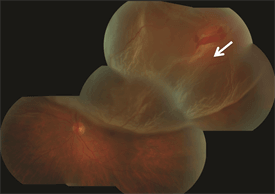
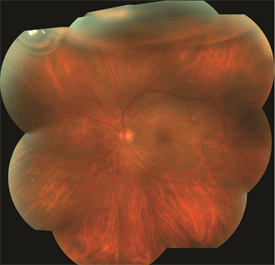
Symptoms in Detail
When the retina is detached from the back wall of the eye, it is separated from its blood supply and no longer functions properly. The typical symptoms of a retinal detachment include floaters, flashing lights, and a shadow or curtain in the peripheral (noncentral) vision that can be stationary (non-moving) or progress toward, and involve, the center of vision. In other cases of retinal detachment, patients may not be aware of any changes in their vision. The severity of the symptoms is often related to the extent of the detachment.
Causes
In general, retinal detachments can be categorized based on the cause of the detachment: rhegmatogenous, tractional, or exudative.
- Rhegmatogenous (reg ma TODGE uh nus) retinal detachments are the most common type. They are caused by a hole or tear in the retina that allows fluid to pass through and collect underneath the retina, detaching it from its underlying blood supply.
Retinal tears can develop when the vitreous gel separates from the retina as part of aging or in patients with abnormal thinning in the peripheral retina (known as lattice degeneration) or occasionally from trauma. - Tractional retinal detachments are caused by scar tissue that grows on the surface of the retina and pulls the retina off the back wall of the eye. This type of retinal detachment may occur from diabetes or other conditions.
- Exudative (ex OO day tive) retinal detachments form when fluid leaks out of blood vessels and accumulates under the retina. This type of retinal detachment is much less common and can occur in eyes with abnormal inflammation or excessive leakage from abnormal blood vessels.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for developing a rhegmatogenous retinal detachment include
- Lattice degeneration (thinning in the peripheral retina, or the area outside of the central retina.)
- High myopia (extreme near-sightedness)
- Advanced age
- Family history of retinal tears or retinal detachment
- Previous retinal detachment
- Previous eye surgery such as cataract surgery
- Trauma
The goal of treatment is to re-attach the retina to the back wall of the eye and seal the tears or holes that caused the retinal detachment. Several approaches can be employed to repair a retinal detachment:
- Scleral buckle—In this surgery, a silicone band is placed outside the eye wall to push the wall of the eye closer to the retinal tear in order to close the tear. The tear is treated with a freezing treatment to induce controlled scarring around the tear and permanently seal it. The fluid under the retina is sometimes removed at the time of surgery.
- Vitrectomy—In this surgery, three small incisions are made in the white part of the eye and fine instruments are manipulated using an operating microscope to remove the vitreous gel that fills the eye and drain the fluid from under the retina. The surgeon may then use a laser or cryopexy to seal the retinal tears or holes. The eye is then filled with a gas bubble to hold the retina in place while it heals.
- Pneumatic retinopexy—In this office-based procedure, a gas bubble is injected into the eye and the patient maintains a specific head posture to position the gas bubble over the retinal tear. The tear itself is sealed either with a freezing treatment at the time of the procedure, or with laser after the retina is re-attached.
- Laser surgery—In certain cases, a retinal detachment can be walled off with laser to prevent the retinal detachment from spreading. This is generally appropriate for small detachments.
Based on the characteristics of the detachment, a retina specialist can determine which approach is most suitable. In general, retinal detachment repairs succeed in about 9 out of 10 cases, though sometimes more than one procedure is required to successfully put the retina back into place.
The visual results depend on each patient’s pre-operative vision and other factors that differ between individual patients. In general, when the center of the retina has not detached before surgery, the post-operative vision tends to be similar to the pre-operative vision. If the central retina is detached prior to surgery, successful re-attachment often leads to vision improvement, though some degree of permanent vision loss may occur.
Diagnostic Testing
Your retina specialist will perform a detailed eye exam, including a careful examination of the peripheral retina. This may include pushing on the outside of the eye (scleral depression) to view the far most peripheral retina to identify any retinal breaks that will need to be treated.
Photographing the retina is sometimes performed to document the extent of the detached retina, and an optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan of the retina can be useful to determine whether fluid has detached the center of the retina (the macula). When a clear view of the retina cannot be obtained by direct visualization, an ultrasound of the eye can be helpful.
Treatment and Prognosis
The goal of treatment is to re-attach the retina to the back wall of the eye and seal the tears or holes that caused the retinal detachment. Several approaches can be employed to repair a retinal detachment:
- Scleral buckle—In this surgery, a silicone band is placed outside the eye wall to push the wall of the eye closer to the retinal tear in order to close the tear. The tear is treated with a freezing treatment to induce controlled scarring around the tear and permanently seal it. The fluid under the retina is sometimes removed at the time of surgery.
- Vitrectomy—In this surgery, three small incisions are made in the white part of the eye and fine instruments are manipulated using an operating microscope to remove the vitreous gel that fills the eye and drain the fluid from under the retina. The surgeon may then use a laser or cryopexy to seal the retinal tears or holes. The eye is then filled with a gas bubble to hold the retina in place while it heals.
- Pneumatic retinopexy—In this office-based procedure, a gas bubble is injected into the eye and the patient maintains a specific head posture to position the gas bubble over the retinal tear. The tear itself is sealed either with a freezing treatment at the time of the procedure, or with laser after the retina is re-attached.
- Laser surgery—In certain cases, a retinal detachment can be walled off with laser to prevent the retinal detachment from spreading. This is generally appropriate for small detachments.
Based on the characteristics of the detachment, a retina specialist can determine which approach is most suitable. In general, retinal detachment repairs succeed in about 9 out of 10 cases, though sometimes more than one procedure is required to successfully put the retina back into place.
The visual results depend on each patient’s pre-operative vision and other factors that differ between individual patients. In general, when the center of the retina has not detached before surgery, the post-operative vision tends to be similar to the pre-operative vision. If the central retina is detached prior to surgery, successful re-attachment often leads to vision improvement, though some degree of permanent vision loss may occur.
Copyright ©2016 The Foundation of the American Society of Retina Specialists. All rights reserved.

